
For lists of symbols categorized by type and subject, refer to the relevant pages below for more. $\displaystyle e = \frac \, dx$įor the master list of symbols, see mathematical symbols. The following table documents some of the most notable symbols in these categories - along with each symbol’s example and meaning. In calculus and analysis, constants and variables are often reserved for key mathematical numbers and arbitrarily small quantities. The LL according to AS 1170 Part 1 (Dead and live load) is 1.5 kPa).Yes. Now we can calculate the weight of the slab:Ĭalculate the live load (LL) for a room of a residential building, size 5.5 m × 3.8 m.
#Newton symbolic calculator how to
analysis calculator nr method by scientific calculator how to solve newton. Density of concrete is 2500 kg/m 3įirst convert mass density in weight density. Calculator Seekh Lo Newton's Method Calculator Newton's. Having converted the mass unit into a weight figure we can now calculate the weight of any structural component or member in newtons by using:Ĭalculate the dead load (DL) for a concrete slab, size 4.0 m × 3.5 m of 172 mm thickness. We need to convert the mass into a weight figure. Newtons Method Calculator Enter the Equation: starting at Solve Computing. Weight (W) = Density × Volume Remember unit for density is kg/m 3 and the unit for volume is m 3 but the unit for weight is measured in newton. To calculate the weight of a component or member we use the formula: However, the most common formulae are listed below:īy closely looking at the units we can easily work out the correct answer of a propblem by substituting the units into the formula.Ĭonsider the following example to work out the weight of a structural component or member: Look for prefixes like k and M in the table above. The meaning of k P and MPa is very important because you'll need to understand the concept of stress and strenght. The following relationship must be learned by heart: 1 Pa If someone borrows 10 dollars from you, you would insist of the same unit, wouldn't you? This simple example points out that the unit is of great important. In SI base units, one Newton is equal to: footnotesize rm 1 N 1 space kg cdot m/s2 1 N 1 kg m/s2 To learn more about force units, go to our force converter. If someone borrowed 10 dollars from you and the borrower settles his debt with 10 cents you wouldn't be happy about it, although the number is identical.

The following will emphasize the importance of the units: With our innovative parser, math syntax is as simple as when you write it on your note. Try to learn them by heart as they will be referred to in different units of competency. Newton Graphing Calculator graph 2D curve and 3D surface by math input like handwriting. Students need to familiarise themselves with quantities, symbols and units. (Many symbols are unfortunately Greek letters) You should try to memorise the symbols and units listedīelow. Symbols and base units used in Competency Units Univariate Derivative-related Symbols y, y, y n, First, second and n th derivative of y in terms of time variable t (Newtons notation), y d 2 y d. Or alternatively, for use with liquids and gases: VOLUME SI unit: cubic metre (m³) 1000 cubic centimetres (cm³) Tables of measures for mass, length, area and volume are set out belowĪREA SI unit: square metre (m²) 100 square millimetres (mm²) Centimetre is a recognised unit of length but centigram is not a recognised unit of mass. * The prefixes `centi' and `deci' are only used with the metre. The Common Prefixes and Units Prefix & Symbol Newton Graphing Calculator graph 2D curve and 3D surface by math input like handwriting. For instance, since the prefix kilo (k) stands for 1000, 1 kilometre (km) equals 1000 metres (m), and any change from metres to kilometres or vice versa simply involves a decimal point or zeros as shown below. This results from the practical system of attaching to unit names (symbols) standard prefixes that stand for some of the powers of 10 such as 0.001 (milli), 1000 (kilo).

One of the main reasons for this is the simple compatibility of the metric system with our world-wide numerals and arithmetic based on the 10 digits and their position relative to a decimal point.
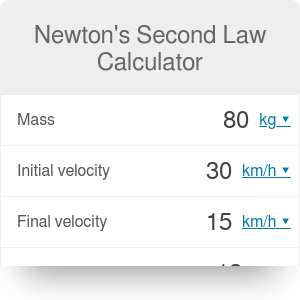
The metric system, and especially that part of it called the SI (le Systéme International d'Unités or, in plain English, the International System of Units), is by far the simplest and most rational system of units devised.

Units and formulas Metric system, symbols & units


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
